The air we breathe is a mixture of gases, the composition of which significantly affects our health. The mass of air affects climate change, the emergence of phenomena such as the greenhouse effect. In addition to atmospheric phenomena, it is...
The air we breathe is a mixture of gases, the composition of which significantly affects our health. The mass of air affects climate change, the emergence of phenomena such as the greenhouse effect. In addition to atmospheric phenomena, it is also worth considering how the composition of air affects the human body.
What is the composition of air?
When analyzing the composition of air, we can distinguish two types of components: fixed and variable. Fixed components are an inherent part of the air, while variable components depend on factors such as changes in the content of sulfur dioxide or carbon dioxide.
The main components of air are nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide. In addition to them, we can also find compounds such as neon, helium, methane, krypton, hydrogen and xenon in the air. Analyzing this composition even more closely, we can also find mineral and organic suspensions in the air, including dust or plant spores.
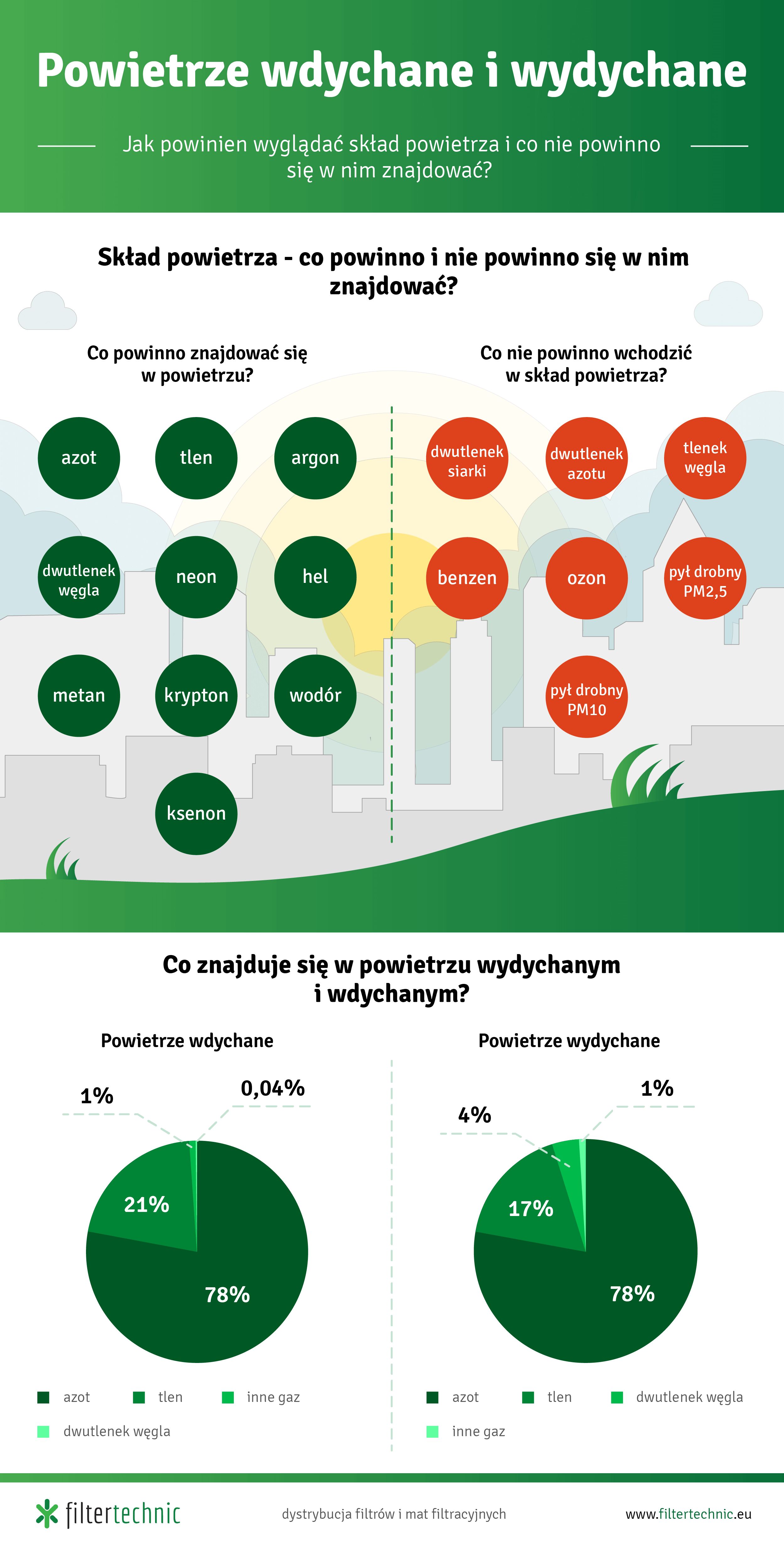
Inhaled and exhaled air - what's in it and what shouldn't be in it?
The air we inhale can be divided into the following components: nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and other gases (1%). In the case of exhaled air, the carbon dioxide content increases and the amount of oxygen decreases: nitrogen (78%), oxygen (17%), carbon dioxide (4%) and other gases (1%).
Unfortunately, the air we breathe increasingly contains substances that shouldn't be there. These components are primarily dust and pollutants, most often originating from human activity - factories, chimneys, furnaces, car exhaust fumes, etc. In such a case, compounds such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ozone, benzene, PM2.5 and PM10 dust begin to appear in the air mass we breathe.
These substances are dangerous to all living organisms - humans, animals and plants. A person inhaling polluted air endangers both their respiratory and circulatory systems, which can result in ailments such as heart rhythm disorders or hypertension.
How to improve air composition?
The air content is controlled using meters that enable effective monitoring of indoor air parameters. Other devices that help assess air quality include: CO2 meters, exhaust gas analyzers, and carbon monoxide and gas detectors. If we do not have this type of equipment, it is worth monitoring the outdoor air quality (using, for example, smog reports) and avoiding walks on days when the concentration of harmful dust is high.





